2.0t03speed
Member
- :
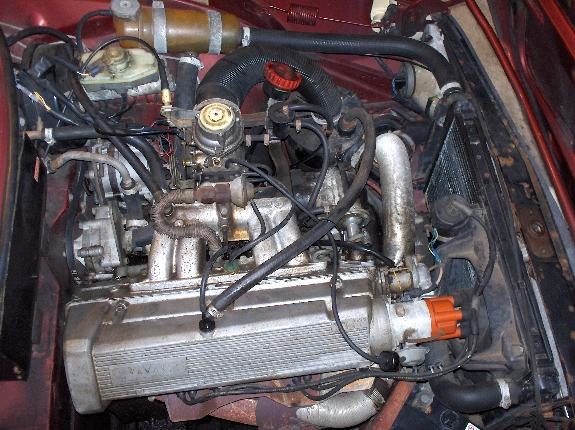
- 08.5 CWP Speed 3
505 mani wasn't just some fly by night diy box. Everything was designed on cad and then ran through a digital flow analysis program. The manifolds make power and i can go on all day about how great they are.
true. some point in the future i want to block mine off and see what happens
@SeR_Cyclops When you say cold start issues, what exactly do you mean?This is because of the EGR gone. My car use to do the same thing, this summer I installed the EGR back like it should have been it fixed all of the cold start issues.
Dude this thread is hella old. But I’ll explain.@SeR_Cyclops When you say cold start issues, what exactly do you mean?